Smartphones and other mobile devices such as tablets and smartwatches are fast becoming more “personal computers” than the PC. People interact with these devices and store more personally identifiable information in them more than any laptop or desktop computer. In today’s technology-driven world, even the first thing to do after waking-up is checking the notification on one’s smartphone. Android alone has 1 billion unique devices each month using the Google Play Store, as per Google’s statistics. With many phones feature a form of digital payment authentication systems like Apple Pay or Google Pay, it becomes the central instrument of commerce and retail for many people.
IDology, cybersecurity and anti-fraud firm, has released their Annual Fraud Report, which details the level of acceptance with the use of insecure mobile devices in the fast-changing market conditions. As Google Pay or Android Pay is connected to someone’s credit line or bank account, the biggest security risks are phishing and fraud websites. IDology highlighted that credit card fraud and the awareness level of the common user.
Firms are implementing their own BYOD (Bring Your Own Devices), but most of these firms are actually not ready when it comes to synthetic identity fraud, account theft, and website fraud.
“The frequency and depth of data breaches, and thus the availability of more personal information than ever on the dark web, have made customer-not present fraud more attractive to bad actors. Whether it’s usernames and passwords, social security numbers, addresses, phone numbers, or account information, criminals can access it. Synthetic identity fraud continues to be an issue, and mobile fraud, such as SMS interception and SIM swapping, has gotten some high-profile attention this year. These fraud forms have been brewing for several years now and are poised to continue growing,” explained John Dancu, CEO of Idology.
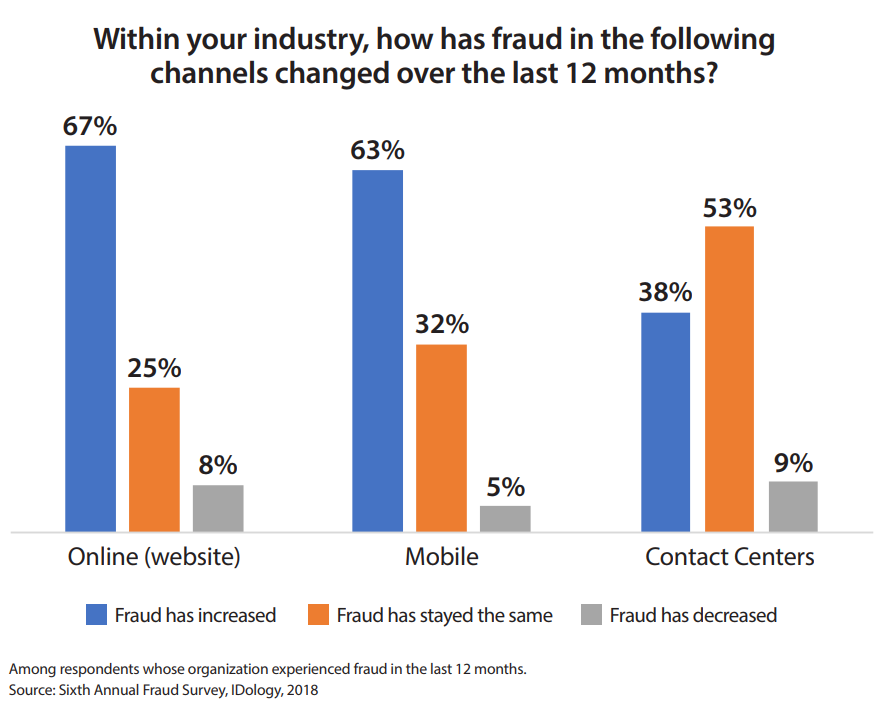
There is a visible indication that the majority of respondents claim that they saw an increase in online fraud, mobile fraud, and continued level of fraudulent calls. “Credit, debit, and prepaid card fraud continues to dominate as the most prevalent form of fraud across industries (67%), affecting everyone from banks and lenders to healthcare organizations. Although 2017 saw a dip in card fraud (down 8% from 2016), it has gone back up by 3% this year. Account takeovers also continued to be a widespread issue, and although they did not increase this year, they have been steadily on the rise since 2014,” said in the report.
According to IDology, the silver lining with the report is the lower percentage of respondents answering as “I don’t know” with the questionnaire. This only means the growth of awareness generally speaking when it comes to cybersecurity issues. The level of ignorance regarding a certain IT issue within the organization has been lessened by 28% compared to last year’s statistics. The only thing organizations have to answer is for their respective IT teams to implement a reasonable training menu for employees. Employees are the front liners of cybersecurity defense strategy for any organization. Expect some resistance to change, but the strategy to educate employees is the most effective method to maintain privacy and security within any organization.
Related Resources:
4 Ways To Keep Your Mobile Device Secure
The Digital War On Mobile Devices Has Solution Providers In A Panic
