Cryptocurrency and the rise crypto-economy have become all the rage in the last 5 years, especially those speculators that are in it for one-time, big-time possibilities. People who even lack enough knowledge about the technology jumped into the bandwagon, and the .com bubble of the late 90s and early 2000s made a repeat.
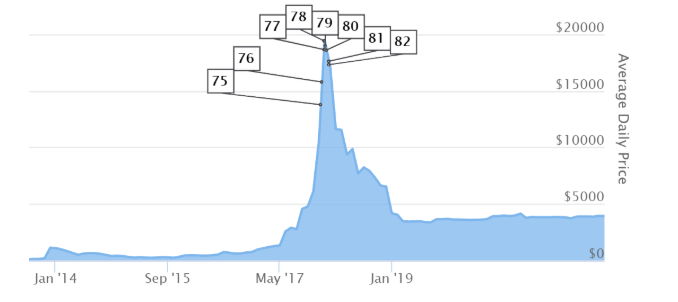
Cryptocurrency exchanges are private enterprises with the goal of being the “money changer” for cryptocurrency and real-world currency. The explosive growth of Bitcoin in 2017-2018 has ended, and there is no real indication that it will reach the level near $20,000 again. After its steep drop, more cryptocurrencies took its place as the “hottest crypto” in town, and the cycle repeats itself.
The reality in the current situation is many people got “scammed” (a term I use loosely in this article), as they exchanged their hard-earned fiat currency for cryptocurrency, in hopes for the latter to increase in value for a short span of time. However, the “hopes” burst like a bubble given that cryptocurrency like fiat money is based on trust. But unlike fiat money, not only the trust of common Joe and Jill that it holds value makes the latter valuable, but by states backing it up. Cryptocurrency is existing just because it exists, it will hold value as long as people will believe in it. However, they don’t have the support of a state-economy, compared to fiat real-world currency being supported by the very economy of its issuing country.
The virtual currency is creating a world dominated by FUD (fear, anxiety, doubt) from its instability. The transaction record of the virtual currency is carried out by mining using sophisticated computers known as ASICs. In Bitcoin mining, a number of mining machines perform a complex and sophisticated calculation at the same time, and the newly minted coin arrives as a reward for answering the hash calculations. If the same calculation is done by more than one mining machine, the final answer should be exactly the same. However, it may be a mistake in calculation or data being tampered with by a malicious person. However, in the end, the person who is given the compensation by mining is correct, it is deemed “agreement of opinion“, and the transaction is approved.
For reasons why virtual currency is hard to use for payment, an explanation from another angle is also possible. The virtual currency needs to make the most important “trust“ for payment instrument from scratch – as no government in the world makes the assurance. Cryptocurrency comes from mining, and subjects to heavy speculation by various groups that have their own agenda to either increase the value or crash its value. In this period, mining cryptocurrency, most especially Bitcoins incur a higher electricity cost than the value of possible virtual coins that can be minted.
Trust issues are also visible when it comes to cryptocurrency exchanges, they are shaky businesses that one day becomes very profitable but can lose everything a day after. This is because their systems in handling hot wallets are in question, not all cryptocurrency exchange services can be trusted. The technology behind cryptocurrency can be dependable, as blockchain is a proven useful in other industries, like engineering and mathematical computations. But the same cannot be said with cryptocurrency exchanges, as such business model is still in its infancy, the world already witnessed some of them already went bankrupt.
At the end of the day, it is the decision of a person if he/she will engage with cryptocurrency trading and who to trust when it comes to the choice of cryptocurrency exchange. There is also no mechanism in many countries on how the criminal justice system works when it comes to cryptocurrency fraud. So the need to be careful in using such new technology is highly encouraged.
